
5 Secrets to Addictive Hypercasual Game Design Rooted in Player Psychology
February 19, 2025
Scaling to 1000X: How to Build a $DAGZ-Style Crypto Token For Exponential Growth In 2025?
February 20, 2025Conducting fair, secure, transparent, and tamper-proof elections has become a pressing challenge even in today’s digital age. For several years, elections have been grappling with security vulnerabilities, fraud risks, and inefficiency that raise questions over election integrity.
According to a report, global voter participation has declined from 65.2% in 2008 to 55.5% in 2023. This decline is attributed to factors such as disinformation, foreign interference, identity verification issues, voter impersonation, double voting, fraudulent voter registration, and more, which have added to electoral challenges and decreased public confidence in electoral processes.
Such challenges can be addressed through blockchain-based voting systems that have lured the interest of many businesses, researchers, government authorities, and practitioners worldwide. Unlike conventional systems controlled by centralized authorities, blockchain-based e-voting platforms operate on a distributed network, making it resistant to manipulation, hacking, and unauthorized alterations.
In this blog, we will delve into how the approach of blockchain development for voting systems can resolve the challenges of conventional voting processes and redefine the future of democracy.
A Look at the Traditional Voting Systems
Before the rise of blockchain-based voting systems, traditional methods like paper ballots and lever machines were widely used to conduct elections.
-
Paper-based voting
Voters in paper-based voting mark their choice on the ballot paper to indicate the candidate or party they wish to vote for. After casting their vote, the ballots are collected and counted manually. This process often involves election officials sorting through large numbers of paper ballots, verifying the authenticity of each vote, and tallying the results.
Paper-based voting can be divided into two categories- Remote paper voting which involves voting by mail or other delivery methods, and on-site paper voting which refers to voting in person at a polling station.
-
Mechanical lever machines
Mechanical levers were first introduced in the 1890s. This type of traditional voting system allows voters to choose their candidates by pressing a lever next to their preferred option. After making their selection, they would pull a larger lever, which added one vote to the chosen candidate’s count and reset the machine for the next voter.
Blockchain-based Voting System- A Revolutionary Step Towards Fair Elections
In the case of a traditional voting system, if the system is compromised, all cast votes can easily be manipulated & misused. A viable solution to overcome such challenges is using the blockchain for elections
“A blockchain-based voting system is a digital voting mechanism that leverages blockchain technology to record, store, and manage votes in a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof manner. Blockchain, the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, is a decentralized and distributed ledger that ensures data integrity and immutability.”
When applied to voting systems, blockchain can fix the shortcomings associated with traditional and electronic voting methods. From stopping illegal voting to strengthening data protection, the use of blockchain for election voting would enhance election integrity, and build public trust in the democratic process.
One can see the difference-
Traditional voting systems involve central authority to cast a vote. If someone wants to modify or change the record, they can do it quickly. In such a case, no one knows how to verify that particular record.

However, in the case of a blockchain-based voting system, one does not have the central authority. All the data is stored in multiple nodes. It is not possible to hack all nodes and change the data. Thus, in this way, one cannot destroy the votes and efficiently verify the votes by tallying with other nodes.
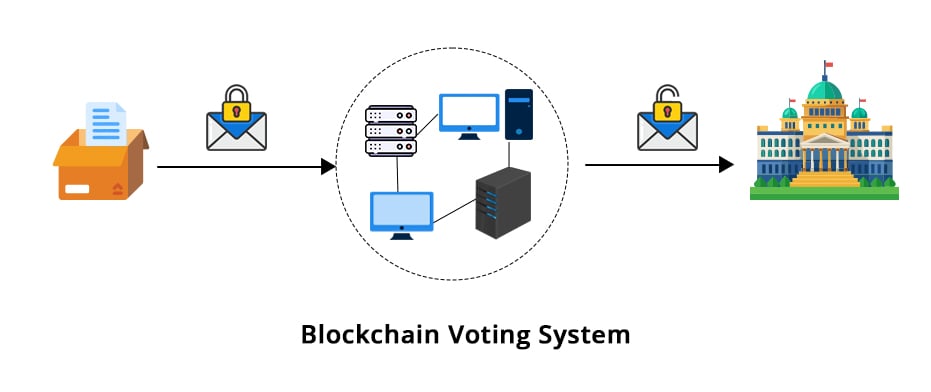
How Does a Blockchain-Based Voting System Work?
Step 1: Voter Authentication
The blockchain-based voting system first verifies the voter’s identity using cryptographic techniques or digital IDs. This helps ensure that only eligible voters participate and cast a vote while preventing duplicate voting.
Step 2: Vote Casting
Once the voter’s identity is verified, the voter casts their vote electronically. The vote cast on a blockchain-based e-voting platform is encrypted to maintain privacy and then recorded as a transaction on the blockchain.
Step 3: Transaction Validation
The transaction (vote) is broadcast to the blockchain network, where it is validated by a number of nodes (computers) using a consensus mechanism (e.g., Proof of Work or Proof of Stake). This ensures that the vote is legitimate and has not been tampered with.
Step 4: Recording on the Blockchain
After the vote validation is done, the vote is then added to a block, which is further linked to the previous block in the chain. It creates an immutable and transparent record of all votes.
Step 5: Result Tallying
At the end of the voting period, the votes are automatically tallied by the blockchain network. The results are publicly accessible and can be verified by anyone, fueling the transparency.
Comparative Analysis: Traditional vs. Blockchain-based Voting Systems
In this section, we will compare traditional and blockchain-based voting systems across several critical parameters.
1. Security
Traditional Voting System Challenge
Traditional voting systems, especially paper-based systems, are prone to human error, tampering, and fraud. Voter impersonation, ballot stuffing, and miscounting are just a few examples of issues that have historically plagued traditional systems. Even electronic voting systems, while faster and more accurate, are still vulnerable to hacking, data breaches, and manipulation.
Blockchain-based Voting System
Blockchain-based e-voting platforms, on the other hand, offer enhanced security due to their decentralized and cryptographic nature. In a blockchain-based voting system, votes are encrypted and linked to a unique cryptographic key that allows only eligible voters to cast their votes. The immutability of the blockchain means that once a vote is recorded, it cannot be altered or tampered with. Additionally, the decentralized nature of blockchain makes it more resistant to attacks, as there is no central point of failure.
2. Transparency
Traditional Voting System Challenge
Transparency is another major concern in traditional voting systems. In many cases, voters and election observers have limited visibility into how votes are counted, which makes it challenging to maintain the integrity of the election results. Although election commissions and auditors perform checks to ensure fairness, there are still concerns about potential manipulation or errors in the counting process.
Blockchain-based Voting System
Blockchain technology offers end-to-end transparency. Every vote cast is recorded on the blockchain-based e-voting platform, and anyone with access to the network can view the transaction. This makes it easier for election observers, political parties, and voters to verify the election results. Because blockchain is immutable, it ensures that the election results cannot be changed after the fact.
3. Efficiency
Traditional Voting System Challenge
Traditional voting systems can be time-consuming, especially in large elections with millions of voters. The process of counting votes, whether by hand or through machines, can take days or even weeks. In addition, logistical challenges such as the transportation of ballots and election officials’ travel can lead to delays and inefficiencies.
Blockchain-based Voting System
Blockchain-based voting systems enable remote voting through secure online platforms that simplify voting. Blockchain’s ability to process transactions quickly means that votes can be counted in real time, which reduces the time it takes to announce election results. Blockchain also eliminates the need for paper ballots and reduces administrative costs and human errors.
4. Voter Accessibility
Traditional Voting System Challenge
Traditional voting systems often require voters to be physically present at polling stations, which can be a significant barrier for people with disabilities, elderly individuals, or those living in remote areas. While absentee voting and online voting options exist in some regions, these systems are not always widely accessible or secure.
Blockchain-based Voting System
Using blockchain for election voting is a strategic approach as it provides greater accessibility to voters. The remote voting advantage through secure blockchain-enabled digital platforms allows eligible voters to participate in elections from anywhere in the world. This can increase voter turnout, particularly in underrepresented or marginalized communities.
5. Cost
Traditional Voting System Challenge
Traditional voting systems, especially paper-based systems, are costly to run. The costs associated with printing ballots, hiring election workers, and setting up polling stations can be substantial. Not only this, the need for extensive security measures is also required to protect physical ballots and electronic voting machines which add to the overall cost.
Blockchain-based Voting System
Blockchain development for voting is an innovative idea to potentially reduce costs. Blockchain-based e-voting platforms eliminate the need for physical ballots and polling stations, as well as streamline the voting and counting processes. No requirement for physical setup lowers the expenses associated with elections. Even blockchain’s security features could reduce the need for costly fraud prevention measures.
6. Voter Privacy
Traditional Voting System Challenge
Voter privacy is a crucial element of any voting system. In traditional systems, privacy is maintained through secret ballots. However, there have been instances of voter intimidation or coercion, especially in countries with less stable political environments. Not only this, but electronic voting systems could potentially expose voter preferences through hacking or other security vulnerabilities.
Blockchain-based Voting System
With its cryptographic security, blockchain technology offers a higher level of voter privacy. In a blockchain-based e-voting system, each vote is anonymized and linked to a unique cryptographic key, ensuring that the voter’s identity remains confidential. The transparency feature of blockchain ensures that while votes are visible on the ledger, they cannot be linked to individual voters.

Notable Projects of Blockchain-Based E-Voting
The following are some notable projects that have either implemented or are actively developing blockchain-based e-voting systems. Take a look!
-
Luxoft
In 2018, Luxoft Holding Inc., a global IT service provider of innovative technology solutions, partnered with the City of Zug and Lucerne University of Applied Sciences in Switzerland to develop the first customizable blockchain-based e-voting system on Hyperledger Fabric.
-
Votem
Votem has made elections easy through its main blockchain-based e-voting platform, Castlron platform. This platform has successfully handled 13 million voters with a proven track record of zero fraud instances, hacking, or attacks, shedding light on the robust security and reliability of the system.
-
Voatz
Voatz is a mobile voting tool that leverages advanced blockchain technology to streamline the election process. To date, this blockchain-based voting system has conducted more than 140 successful live elections in 7 countries. In its largest election, more than 1.7 million votes were cast.
-
Polys
Polys is a blockchain-based voting system that governments, education institutions, businesses, and communities can leverage to facilitate transparent and secure elections. Customers can select from four types of ballots to build and run their voting processes. It also offers a hardware solution for onsite voting.
-
DecentraVote
DecentraVote is a privacy-preserving blockchain-based e-voting platform for virtual general meetings. Developed by the Blockchain Lab of the German IT company iteratec GmbH, DecentraVote plays a crucial role in the adoption of decentralized e-voting systems for governance on a corporate level.
Conclusion
The debate between traditional and blockchain-based voting systems is not about choosing one over the other but rather about finding the most effective way to ensure secure, transparent, and accessible elections. While traditional systems have stood the test of time, they are increasingly struggling to meet the demands of the digital age.
The blockchain-based voting system offers a promising alternative that upholds the principles of democracy—fairness, transparency, and inclusivity. Several governments, authorities or communities worldwide have embraced the power of blockchain for election voting.
As a leading blockchain development company, Antier develops secure, scalable, and efficient blockchain-based voting systems that empower governments and enterprises to revolutionize elections with tamper-proof digital voting systems. Partner with us today for an ingenious blockchain-based e-voting system that ensures the future of voting is fair, inclusive, and verifiable.



