
Decoding Advanced Concepts & Future White Label Crypto Wallet Trends
April 26, 2024
Which Top 5 High-Performance Crypto Gaming Tokens Should You Invest in 2024?
April 30, 2024In today’s hyper-connected world, our sensitive information constantly zips across networks. From credit card details to medical records, this data is a goldmine for cybercriminals. Organizations have a responsibility to safeguard this information, but traditional security measures often have limitations. This is where tokenization emerges as a powerful weapon in the fight against data breaches.
What is Tokenization and How Does it Work?
Data tokenization is the process of replacing sensitive data with a non-sensitive equivalent, called a token. Imagine a high-security vault where your credit card number is the treasure. Tokenization creates a unique key (the token) that allows authorized access for transactions, without revealing the actual credit card information stored securely within the vault.
There are two main types of tokenization:
- Deterministic Tokenization: A mathematical algorithm generates the token based on the original data. This allows authorized personnel to reverse the process (reverse tokenization) to access the original data when necessary, such as for fraud investigations.
- Non-deterministic Tokenization: Here, a completely random token is generated, offering even stronger security. However, unlocking the original data becomes impossible – a good option for information that never needs retrieval.
Asset Tokenization Process for Digital Security
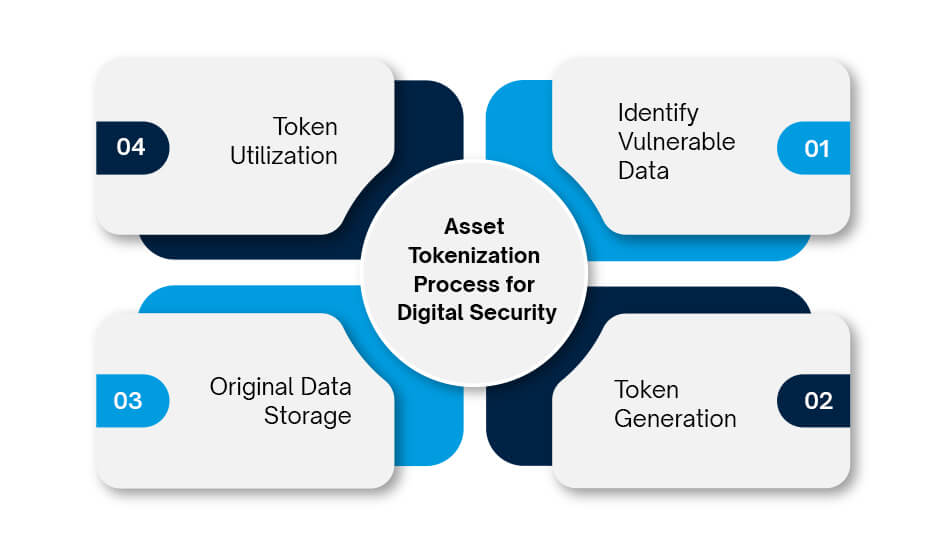
1. Identify Vulnerable Data: The first step involves identifying the sensitive data points within a system that need protection. In case of financial data, it can include credit card information, bank account numbers, and other financial details are prime targets. In terms of healthcare records, it is patient information like medical history, diagnoses, and treatment details that require strict protection.
2. Token Generation: A specialized algorithm crafts a unique, non-reversible token to replace the flagged data. This token has no inherent value to hackers and acts as a stand-in for the original information.
3. Original Data Storage: The original sensitive data is securely stored in a separate, often restricted location. This ensures that even if hackers infiltrate a system, they’ll only encounter the meaningless tokens, not the valuable information itself.
4. Token Utilization: The token is used for various purposes where the original data isn’t needed. Imagine processing payments online, verifying your identity at a healthcare provider, or accessing online accounts, all without exposing your sensitive data.
The Tokenization Shield: Protecting Your Data in a Digital Age
Data for tokenization offers a multi-layered security approach, providing substantial benefits for organizations and individuals:
- Reduced Breach Risk: Data breaches are a constant threat. With tokenization, even if hackers gain access to a system, they’ll only find meaningless tokens, rendering the stolen data useless for identity theft or financial fraud.
- Enhanced Security: By isolating and securing sensitive data, tokenization minimizes the attack surface for potential breaches. Hackers have less valuable data to target.
- Compliance Champion: Many regulations mandate organizations to safeguard sensitive data. Tokenization helps organizations meet these requirements and avoid hefty fines.
- Streamlined Processing: Tokens can be used for many data processing tasks without compromising security. This improves efficiency as sensitive data no longer needs to be readily accessible within systems.
- Data Sharing Made Safe: Tokenization allows organizations to securely share data with third parties. This fosters collaboration, data analysis, and better services for customers. Imagine healthcare providers securely sharing patient information for better diagnosis and treatment, or businesses collaborating on projects while keeping sensitive data confidential.
Real-World Protectors: Tokenization in Action
Tokenization is already making waves across various industries, safeguarding sensitive data in real-world applications:
- Payment Processing: As mentioned earlier, credit card information is commonly tokenized for secure online transactions. Instead of your actual card details, merchants receive a token for processing payments. This protects your financial information and reduces the risk of fraud.
- Healthcare Heroes: Patient information like medical records can be tokenized. Doctors and authorized personnel can access the data using the token, protecting patient privacy while ensuring secure healthcare delivery. Imagine securely sharing medical records between hospitals for better treatment or participating in clinical trials without compromising your privacy.
- Customer Guardians: Personal data like names, addresses, and phone numbers can be tokenized. This safeguards against identity theft and data breaches. Loyalty programs and online accounts can leverage tokens to identify customers without exposing their personal information. Imagine earning rewards points at your favorite store using a tokenized identifier instead of your full name and address.
- API Gatekeepers: Tokens can be used to authenticate users and secure access to APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that exchange sensitive data. This ensures only authorized applications can access the information they need. Imagine securely connecting your fitness tracker app to a health insurance platform using a token instead of sharing your login credentials.
Tokenization vs. Encryption: Securing Your Data
While both tokenization and encryption play a crucial role in data security, they achieve this goal in fundamentally different ways. Here’s a detailed breakdown of each:
Choosing Between Tokenization and Encryption:
Tokenization acts as a data replacement service. It substitutes sensitive elements, like credit card numbers, with meaningless tokens – essentially random strings with no inherent value. Even if intercepted, these tokens are useless to attackers. This significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and streamlines compliance with data privacy regulations by removing sensitive data from core systems. Additionally, tokenization can sometimes preserve the original data format, simplifying integration with existing systems.
Encryption, on the other hand, adopts a cloaking approach. It scrambles data using complex algorithms and a secret key, rendering it unreadable (ciphertext) without the key. While authorized users can decrypt the data for access, retrieving the original information from a token can be a more involved process. Encryption excels at securing data in transit between systems and protects data at rest on devices like laptops and mobile phones.
The best choice between tokenization and encryption depends on the specific use case:
Use Tokenization for:
- Protecting sensitive data at rest (stored within systems)
- Simplifying data privacy compliance
- When data format preservation is important (e.g., credit card processing)
Use Encryption for:
- Securing data in transit (being transmitted)
- When authorized users need to decrypt the data?
- Protecting data on devices (laptops, mobile phones)

The Evolving Landscape: The Future of Tokenization
Tokenization is a rapidly evolving technology with immense potential for securing our digital world. Here’s a glimpse into what we can expect:
- Cloud Integration: Tokenization solutions will seamlessly integrate with cloud platforms, ensuring secure data storage and processing in the cloud environment. This will enable businesses to leverage the scalability and flexibility of the cloud while maintaining robust data security.
- Standardization and Interoperability: Industry-wide standards and interoperable tokenization solutions will enable easier data sharing across different platforms. Imagine seamlessly sharing medical records between hospitals or collaborating with partners without compromising data security. This will foster greater collaboration and innovation across various sectors.
- AI and Machine Learning Powerhouse: AI and machine learning can be used to analyze tokenized data and identify potential threats. This proactive approach will further enhance security by predicting and preventing breaches before they even occur. Imagine AI algorithms constantly monitoring tokenized data patterns to detect suspicious activity and prevent cyberattacks.
Beyond Security: Additional Advantages of Tokenization
While enhanced security is the primary benefit, tokenization offers additional advantages:
- Improved User Experience: Tokenization can streamline processes like online payments and identity verification, making them faster and more convenient for users.
- Reduced Costs: Organizations can save money by minimizing the risk of data breaches and the associated financial penalties. Additionally, streamlined data processing can lead to operational cost reductions.
- Privacy by Design: Tokenization fosters a “privacy by design” approach, where data privacy is considered from the very beginning of any system or process.
Conclusion
Tokenization is a transformative technology that empowers organizations and individuals to navigate the digital age with greater confidence. By replacing sensitive data with secure tokens, tokenization safeguards our information, fosters trust, and paves the way for a more secure digital future. As the technology evolves and integrates with other advancements like AI and cloud computing, we can expect even more robust data security solutions that protect our privacy and enable secure and seamless interactions in the digital world.



