Asset tokenization is transforming the landscape of ownership and investment. By converting physical and digital assets into tokens on a blockchain, we create new opportunities for liquidity and fractional ownership. However, the methods for tokenization differ significantly. In this blog, we’ll explore the distinctions between on-chain and off-chain asset tokenization, looking at their unique benefits and practical applications.
What is Asset Tokenization?
Asset tokenization involves turning ownership rights of both tangible and intangible assets into digital tokens that exist on a blockchain. This approach allows for a more efficient and transparent way to manage assets, expanding investment opportunities across various asset classes, such as real estate, art, commodities, and stocks.
The Role of Blockchain
Blockchain technology is at the heart of asset tokenization. It provides a secure, decentralized ledger that records transactions and ownership details. This transparency fosters trust among all parties involved, making blockchain a natural fit for tokenization.
On-Chain Asset Tokenization
What is On-Chain Tokenization?
On-chain asset tokenization means that tokens are fully recorded and managed on a blockchain. Every piece of information about the asset—ownership, transaction history, and legal rights—is stored directly on the blockchain, ensuring high levels of transparency and security.
Key Features of On-Chain Tokenization
Transparency: All transactions are visible on a public ledger, allowing stakeholders to verify ownership and history easily.
Security: Utilizing cryptographic techniques, on-chain tokenization secures ownership rights, making them tamper-proof.
Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts automate processes like ownership transfers and compliance checks, reducing the need for intermediaries.
Use Cases for On-Chain Tokenization
On-chain tokenization excels in situations where transparency and liquidity are vital. Here are a few noteworthy applications:
Real Estate Investment: The real estate market often requires significant capital and can be illiquid. Tokenizing properties allows investors to purchase fractional ownership, making it more accessible. This not only democratizes investment in real estate but also enhances liquidity by facilitating trading on secondary markets.
Art and Collectibles: Tokenization in the art world enables artists to tokenize their works, allowing multiple investors to share ownership of a piece. This broadens access to art investments and helps verify authenticity, adding security to transactions.
Financial Instruments: On-chain tokenization simplifies trading for stocks and bonds. Converting shares into tokens can reduce settlement times and improve market accessibility, enhancing the trading experience for investors.
Supply Chain Management: Tokenizing goods allows companies to track and verify the authenticity of products as they move through the supply chain, reducing fraud and increasing efficiency.
Advantages of On-Chain Tokenization
On-chain tokenization has several key benefits:
Liquidity: It enhances liquidity by enabling the trading of traditionally illiquid assets on secondary markets.
Global Access: On-chain tokenization opens doors for investors around the world, allowing broader participation in various markets.
Cost Efficiency: Reduced administrative costs and faster settlement times can lead to lower transaction fees for both issuers and investors.
Data Integrity: With all transactions recorded on the blockchain, ownership records are kept accurate and up to date, minimizing disputes.

Off-Chain Asset Tokenization
What is Off-Chain Tokenization?
Off-chain asset tokenization refers to tokens that represent ownership of assets managed outside the blockchain. Although the token exists on a blockchain, the underlying asset is tracked and managed through traditional systems or alternative databases, offering its own set of advantages.
Key Features of Off-Chain Tokenization
Simplicity: Implementing off-chain tokenization can be straightforward, especially for businesses that already have established asset management systems. It makes it an appealing option for companies looking to adopt tokenization without a complete overhaul.
Flexibility: Off-chain systems can integrate various data sources and adapt to existing regulatory frameworks, allowing companies to tailor their tokenization strategies to fit specific needs.
Use Cases for Off-Chain Tokenization
Off-chain tokenization is particularly effective in situations where speed and regulatory compliance are key. Here are some notable applications:
Private Equity and Venture Capital: In these fields, firms can tokenize shares in a fund, simplifying ownership transfers while managing underlying assets off-chain. It allows investors to benefit from tokenization while maintaining traditional structures.
Loyalty Programs: Companies can create loyalty points that exist as tokens but are managed through conventional databases. This enhances customer engagement by allowing users to trade or redeem their points more conveniently.
Supply Chain Verification: Tokens representing goods can be managed off-chain while utilizing blockchain for verification. This hybrid approach allows businesses to maintain control over their data while leveraging blockchain’s strengths for authenticity checks.
Digital Identity Management: Off-chain tokenization can streamline the management of digital identities. By creating tokens that represent various identity attributes, companies can simplify KYC (Know Your Customer) processes while ensuring regulatory compliance.
Advantages of Off-Chain Tokenization
The benefits of off-chain tokenization include:
Faster Transactions: Off-chain systems can execute transactions more quickly, often without requiring blockchain consensus, which is crucial for businesses needing rapid processing.
Easier Compliance: Managing assets off-chain allows companies to navigate regulatory requirements more smoothly, simplifying the compliance process.
Lower Initial Costs: Off-chain tokenization offers a gradual approach for businesses not ready to fully embrace blockchain technology, allowing them to experiment before fully committing.
Adaptability: Off-chain solutions can be integrated with existing systems, making the transition smoother for companies adopting tokenization.
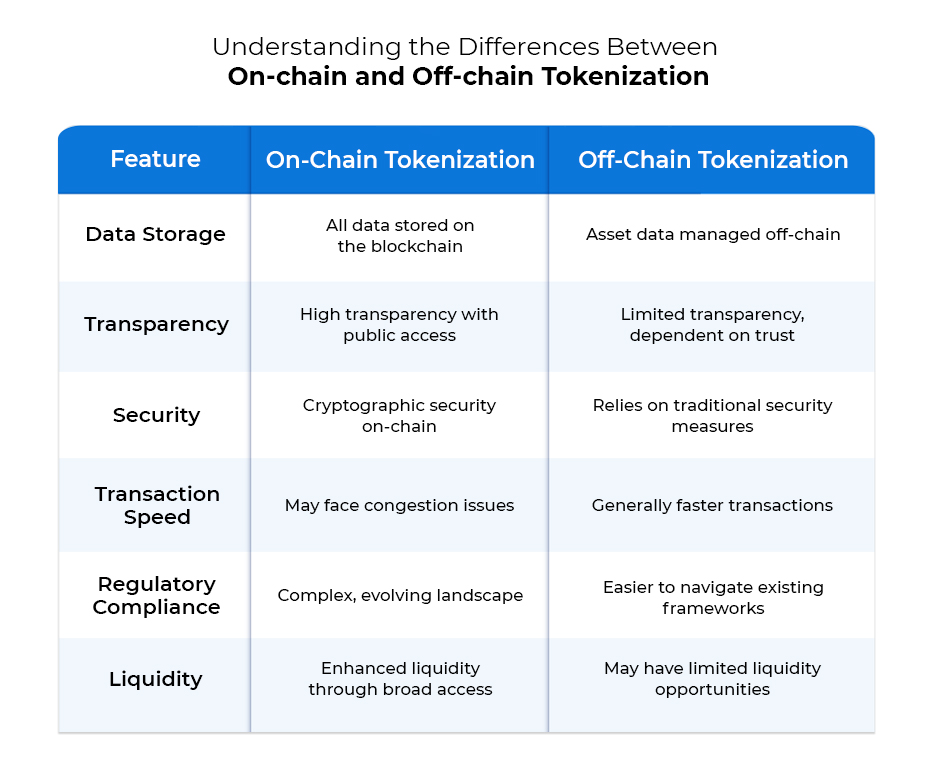
Key Differences Between On-Chain and Off-Chain Tokenization
Understanding the differences between on-chain and off-chain tokenization can help businesses and investors make informed decisions about which method best suits their needs. Here’s a summary of the key distinctions:
Conclusion
On-chain and off-chain asset tokenization enjoy specific benefits while serving distinct purposes in the investment world. On-chain is best for applications with requirements of transparencies, security, and liquidity, like real estate, art, and more kinds of financial instruments. Off-chain will, on the other hand, be best for situations where speed, flexibility in regulation, and ease of putting into practice are key.
As the asset tokenization landscape continues to shift and evolve, understanding the key differences will endow businesses and investors with the knowledge to choose the right approach toward their goals. Whether you are interested in tokenizing real estate, art, or financial instruments, your choice between on-chain and off-chain is going to significantly impact the logic of your strategy and outcomes.
Keeping oneself updated with these changes, therefore, is the key to fully benefiting from asset tokenization in the evolving market. Want to develop an asset tokenization platform that is robust, secure, and scalable? Get in touch today!