
Decentralized Governance in Real Estate: The Role of DAOs in Tokenized Properties
March 25, 2025
What Makes Ethereum L2 Ideal for Scalable DeFi Lending Platform Development in 2025?
March 25, 2025Two key developments, Account Abstraction (AA) and Chain Abstraction (ChA), are the transformative innovations introduced in blockchain space with the motive of improving user experience, security, and scalability. However, at the same time, they are often misunderstood as competing technologies. In reality, both serve distinct yet complementary purposes in Web3.
This blog covers an in-depth comparison of Chain Abstraction vs Account Abstraction. We will explore their functionalities, highlight their key differences, and demonstrate how these innovations can collaborate to drive Web3’s growth in the Abstraction Age.
Understanding Chain Abstraction
What is Chain Abstraction?
Chain Abstraction (ChA) is a multi-chain interoperability solution that enables users to interact across distinct blockchains without manually bridging assets or switching networks. It abstracts the complexities of multi-chain transactions and makes blockchain interactions seamless.
Key Features of Chain Abstraction
- Automatic liquidity routing across the chains eliminates the need for manual bridging.
- Cross-chain gas payments allow users to pay gas fees in any token on any chain.
- Abstracted network switching allows dApps to operate across different blockchains and eliminates the need for users to manually switch chains.
How Chain Abstraction Works
Chain Abstraction leverages cross-chain messaging protocols (such as LayerZero, Axelar, and Wormhole) to enable seamless multi-chain interactions. The process involves:
- A user initiates a transaction on one blockchain without knowing which chain their assets reside on.
- The ChA infrastructure routes liquidity and processes the transaction across multiple chains in the background.
- The transaction is executed on the destination chain, with gas fees handled automatically.
The chain abstraction implementation removes the friction of blockchain interoperability and makes Web3 as intuitive as Web2.
Let’s understand this with an example-
Imagine a user holding 400 USDC on the Arbitrum blockchain has the intent of earning 20% return over it. In the chain abstraction model, the user’s intent is collected and sent to solvers who further find the best ways to fulfill those intents. The solver proposes several options for the user. Now what’s so unique about this mechanism is that once a user selects an option, even if it involves another blockchain, they don’t need to worry about acquiring native tokens for bridging USDC, transaction fees, or swapping tokens. Some chain abstraction solutions even include built-in MEV protection. All these complexities are handled behind the scenes, which makes the user experience smooth and uninterrupted.
Some Notable Chain Abstraction Projects
- Arcana Network
- Socket
- Particle Network
- Safe
- NEAR Protocol
- Connext
- Etherspot and others.
Get comprehensive insights into key chain abstraction projects here.
Understanding Account Abstraction
What is Account Abstraction?
Account Abstraction (AA) simplifies blockchain interactions by allowing smart contracts to control accounts instead of relying solely on Externally Owned Accounts (EOAs). Traditionally, EOAs (like MetaMask wallets) require private keys for transactions and gas fees in native tokens. With account abstraction, smart contract wallets can customize transaction logic, with features like gasless transactions, multi-signature security, automated payments, and social recovery.
AA was standardized with ERC-4337 transactions, which introduced decentralized components like Paymasters, Bundlers, and smart contract wallets and made AA accessible without modifying Ethereum’s core protocol.
Key Features of Account Abstraction
AA introduces smart contract-based wallets that automate many of these complexities, enabling:
- Gasless transactions via Paymasters allow users to pay fees in any token.
- Session keys for automated transaction signing without repeated approvals.
- Social recovery mechanisms, which replace seed phrases with multi-factor authentication and increase security.
- Batch transactions enable multiple actions to be done in a single click.
How Account Abstraction Works
Instead of relying on EOAs that require private key management, AA enables modular smart contract accounts to execute transactions autonomously. This means:
- Users sign up with social logins or biometric authentication instead of private keys.
- Transactions are bundled and processed efficiently, which reduces gas fees.
- Gas payments can be abstracted by simply allowing dApps to sponsor fees or accept payments in any token.
This results in a smoother onboarding process, especially for users unfamiliar with blockchain.
Let’s understand this with an example-
Imagine you have a crypto wallet, but instead of dealing with complex private keys and gas fees in ETH, your wallet works more like a smart account that automates everything for you. This is what account abstraction (AA) does. It transforms traditional Ethereum accounts into programmable smart contracts, which makes transactions more user-friendly.
For example, let’s say a user wants to send USDT from their wallet, but they have no ETH for gas fees. Normally, they need to buy ETH first. With account abstraction, their smart wallet allows them to pay gas fees in USDT or any token they hold. Additionally, instead of remembering a private key, the user can set up multi-factor authentication or recover their wallet using trusted friends or devices.
Some Notable Account Abstraction Projects
- Argent X
- Ambire Wallet
- Biconomy
- Etherspot
- Safe (formerly Gnosis Safe) and more.
Comparing Account Abstraction and Chain Abstraction
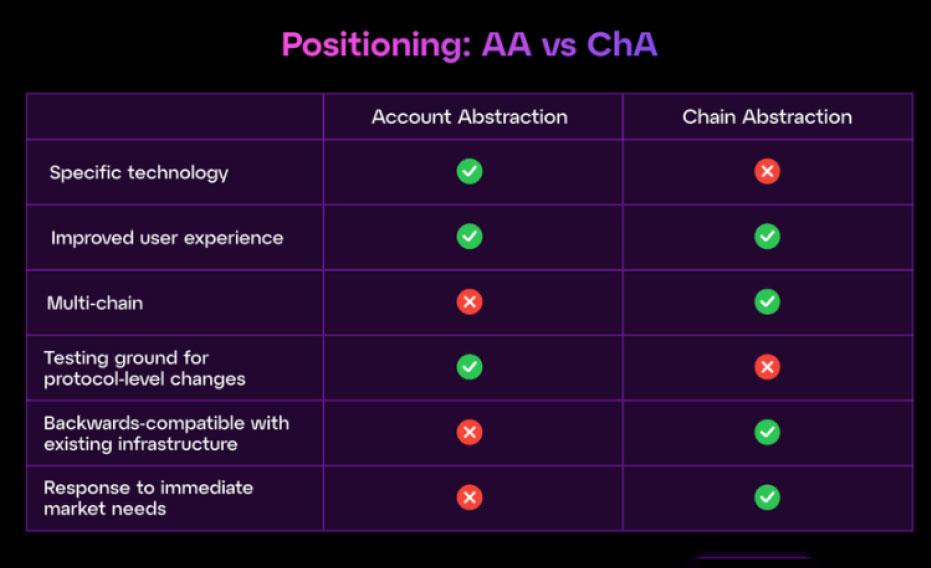
Direct comparison of the positioning of chain abstraction and account abstraction.
Account Abstraction (AA) and Chain Abstraction (ChA) are two pivotal concepts in the blockchain ecosystem, each aiming to enhance user experience and system functionality. Here’s a comparative analysis based on the specified aspects:
-
Specific Technology
Account Abstraction (AA): AA introduces programmable accounts that offer the features, such as gasless transactions, multi-factor authentication, and social recovery. This is achieved through mechanisms such as smart contract wallets and standards like ERC-4337.
Chain Abstraction (ChA): ChA is more of a conceptual framework aimed at simplifying interactions across multiple blockchains by abstracting the complexities of each chain, rather than a specific technological implementation.
-
Improved User Experience
Account Abstraction (AA): With features like gasless transactions and enhanced security through programmable accounts, AA significantly streamlines the user experience.
Chain Abstraction (ChA): ChA enables seamless interactions across different blockchains and eliminates the need for users to manage multiple wallets or understand the intricacies of each chain. This is what fuels the user experience.
-
Multi-chain Support
Account Abstraction (AA): AA primarily focuses on enhancing account functionalities within a single blockchain environment and does not inherently provide multi-chain support.
Chain Abstraction (ChA): ChA provides a unified interface for users and developers, which facilitates interactions across multiple blockchains,
-
Testing Ground for Protocol-Level Changes
Account Abstraction (AA): AA serves as a testing ground for protocol-level changes that allow experimentation and implementation of new account functionalities within the blockchain protocol.
Chain Abstraction (ChA): ChA focuses on creating a seamless experience across different blockchains and does not serve as a testing ground for protocol-level changes within individual blockchains.
-
Backward Compatibility with Existing Infrastructure
Account Abstraction (AA): Implementing AA often requires significant changes to the existing blockchain infrastructure, which may not be backward compatible.
Chain Abstraction (ChA): ChA aims to integrate various blockchains without necessitating changes to their existing infrastructures, hence it ensures backward compatibility.
-
Response to Immediate Market Needs
Account Abstraction (AA): While AA offers long-term benefits, its implementation is complex and may not address immediate market demands.
Chain Abstraction (ChA): ChA addresses the immediate need for interoperability among various blockchains, responding directly to current market demands for seamless multi-chain interactions.
In summary, both Account Abstraction and Chain Abstraction aim to simplify the blockchain ecosystem, but they do so in distinct ways.

Are AA and ChA Competing or Complementary?
A key misconception is that Account Abstraction and Chain Abstraction are competing technologies. In reality, they address different pain points in blockchain usability and perfectly complement each other to create a frictionless Web3 experience.
How They Work Together:
- AA removes gas fees, private key management, manual approvals hurdles, and the user’s interaction with wallets.
- ChA eliminates the complexity of interacting with multiple blockchains. Users don’t need to bridge assets or switch networks.
- When combined, they create a unified, seamless Web3 experience—where users can interact with dApps without worrying about wallets, gas, or networks.
For example, a Chain Abstracted dApp using Account Abstraction would allow:
- A user to pay gas fees in any token on any chain.
- Transactions are to be automated and bundled. No need for any approval steps.
- Network switching is invisible, which allows users to interact with dApps without blockchain knowledge.
Together, chain abstraction and account abstraction adoption make blockchain as seamless as traditional applications.
Conclusion
Rather than competing, account abstraction and chain abstraction complement each other to create a truly seamless blockchain experience. On one side, where AA improves wallet usability by removing the complexities of gas fees, private key management, and manual approvals, ChA’s effortless cross-chain interactions remove network switching and bridging.
AA and ChA work together to drive the next wave of Web3 adoption and make blockchain technology as easy to use as the internet. Partner with an experienced blockchain development company to harness the potential of AA and ChA. Whether you’re building a user-friendly wallet, an interoperable dApp, or a cross-chain DeFi platform, Antier’s expert guidance ensures seamless integration of AA and ChA and helps you unlock a frictionless, scalable, and future-ready blockchain experience.
Step into the next phase of Web3 with the right expertise of Antier by your side! Connect with our team today for a free consultation!



