Decentralized Finance development has taken the financial world by storm, offering innovative solutions that aim to replace traditional financial intermediaries. However, one of the challenges facing the DeFi ecosystem is the fragmentation of blockchain networks. DeFi applications often exist on different blockchains, limiting interoperability and liquidity. DeFi bridges have emerged as a crucial component to overcome these limitations; they allow seamless communication and asset transfers between different blockchain networks.
In this blog, we will explore DeFi bridges comprehensively, covering their importance, architecture, best cross-chain crypto bridges and everything you need to know about this vital technology.
Understanding DeFi Bridges
What Are DeFi Bridges?
DeFi bridges are software protocols that facilitate the movement of assets and data between different blockchain networks, enabling interoperability within the decentralized finance ecosystem. They act as connectors that bridge the gap between separate blockchain networks, allowing users to transfer assets seamlessly from one chain to another.
The Importance of Interoperability in DeFi
Interoperability is crucial for the growth and expansion of the DeFi ecosystem. It allows users to access a wider range of assets and applications, leading to increased liquidity, improved user experience, and enhanced functionality. Without bridges, DeFi would remain isolated on individual blockchains, limiting its potential.
Benefits of DeFi Bridges
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) bridges offer several significant benefits that contribute to the growth and expansion of the DeFi ecosystem. These benefits include:
- Interoperability: DeFi bridges enable seamless communication and asset transfers between different blockchain networks. This interoperability breaks down silos and allows users to access assets and applications on various blockchains, increasing the overall functionality of the DeFi ecosystem and decentralized applications Development.
- Access to Multiple Blockchains: With DeFi bridges, users can access and interact with decentralized applications (dApps) and assets on multiple blockchains, expanding the range of opportunities available to them. This access encourages innovation and diversification within the DeFi space.
- Cross-Chain Asset Transfers: DeFi bridges facilitate cross-chain asset transfers, allowing users to move assets like Bitcoin or Ethereum from their native blockchains to other networks. This is especially valuable for users looking to leverage their assets in DeFi protocols, yield farming, or trading.
- Increased Liquidity: DeFi bridges enhance liquidity by connecting assets from different blockchains. As a result, users can trade or access assets seamlessly across chains, reducing slippage and improving trading experiences.
- Optimized Yield Farming: Yield farmers can optimize their strategies by moving assets across different DeFi protocols on various blockchains. DeFi bridges make it possible to capture the best yield opportunities, leading to more efficient capital allocation and potentially higher returns.
- Diverse DeFi Ecosystems: DeFi bridges allow users to interact with decentralized applications and protocols on various blockchains, each with its unique features and offerings. This diversity promotes competition and innovation within the DeFi ecosystem, benefitting users with more choices and improved services.
- Asset Diversification: DeFi bridges enable users to diversify their assets across multiple blockchains, reducing concentration risk. This diversification can help users manage risk and protect their investments.
- Improved User Experience: DeFi bridges enhance the overall user experience by simplifying the process of moving assets between blockchains. Users can access and manage assets on different networks without needing to navigate complex technical procedures.
- Security: Trustless DeFi bridges, which rely on smart contracts and decentralized custody solutions, provide a high level of security and transparency. Users can verify the functionality of these bridges on the blockchain, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities.
- Ecosystem Growth: DeFi bridges contribute to the growth and adoption of the DeFi ecosystem. As more assets and users participate in DeFi activities across different chains, the ecosystem becomes more robust and resilient.
- Innovation: DeFi bridge projects continue to innovate and develop new solutions to address challenges and improve interoperability. This ongoing innovation benefits the entire blockchain and DeFi space.
- Financial Inclusion: DeFi bridges can help facilitate financial inclusion by providing users from various regions and with diverse assets access to decentralized financial services and opportunities.
Types of DeFi Bridges
There are two main types of DeFi bridges: trusted and trustless.
Trusted Bridges
Trusted bridges depend upon a central entity or system for their operations. They have trust assumptions with respect to the custody of funds and the security of the bridge. Users mostly rely on the bridge operator’s reputation. Also, users need to give up control of their crypto assets.
Trustless Bridges
Trustless bridges operate using smart contracts and algorithms. They are trustless, i.e., the security of the bridge is the same as that of the underlying blockchain. Through smart contracts, trustless bridges enable users to remain in control of their funds.
Unlock a World of Financial Possibilities with DeFi Bridges!
Schedule Free DemoHow Do DeFi Bridges Work?
DeFi bridges leverage a combination of smart contracts, oracles, and custodians to facilitate cross-chain transactions. When a user initiates a transaction on one blockchain (e.g., Ethereum) to move assets to another (e.g., Binance Smart Chain), the bridge locks the assets on the source chain and issues corresponding tokens or assets on the destination chain. These tokens are pegged to the original assets and can be redeemed back through the bridge when needed.

Transaction Flow through the bridge:
- User initiates the transaction on the Polygon bridge contract.
- The validators get the transfer event, and the contract decides the transaction is valid or not valid based on the validation threshold.
Here, we can use validators for 2 cases for validation:
- Case 1: We can select the one validator for the validation randomly from the available validators.
- Case 2: In this case, we have to set the threshold for the validation i.e. we have to choose/set the no.of validations required for the validation.
- Post validation will trigger the bridge contract on the Strakware bridge contract which will initiate minting on the token contracts.
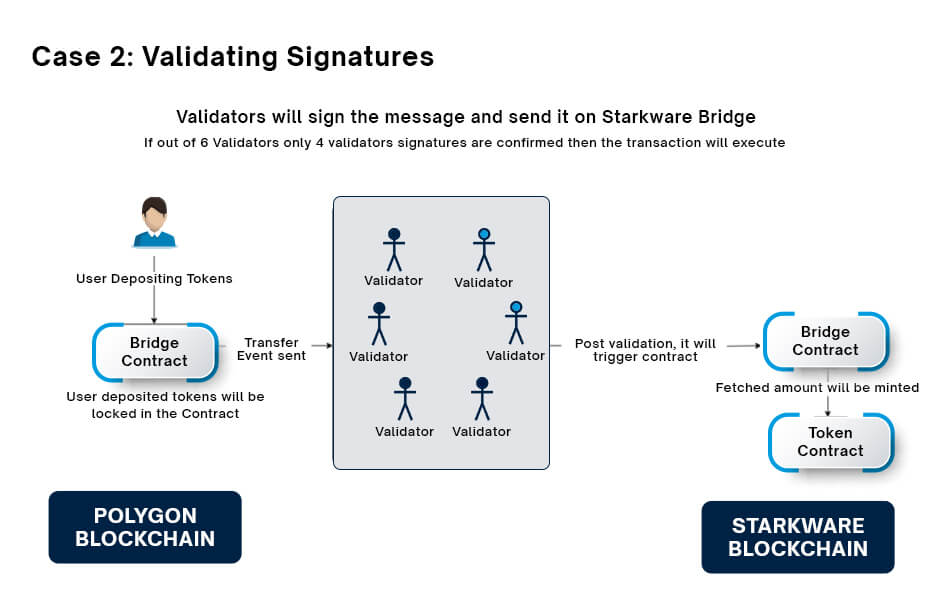
In this scenario:
● User initiates the transaction on the Polygon bridge contract.
● The validators get the transfer event and sign the message.
● These signatures will be verified by the script
● If 4 out of 6 validators’ signatures got verified then the data will be passed to the Startkware
● The tokens on Polygon get locked and tokens on Startkware get released to the user
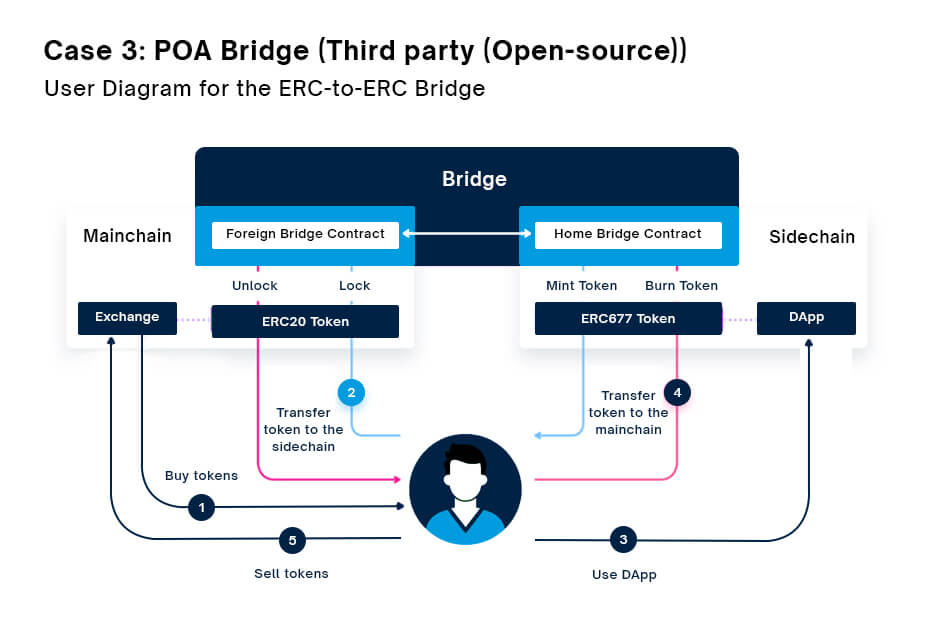
POA Bridge uses a smart contract to facilitate cross-chain transfers. When a user wants to transfer assets from Ethereum to POA Network, they send their assets to the smart contract. The smart contract then mints an equivalent amount of assets on the POA Network and sends them to the user’s POA Network address.
- The user initiates the transaction on the POA Bridge contract.
- The validators on the POA Network blockchain get the transfer event and sign the message.
- The signatures are verified by the script.
- If 4 out of 6 validators’ signatures are verified, then the data is passed to the Foreign Bridge Contract on the Ethereum blockchain.
- The tokens on POA Network are locked and tokens on Ethereum are released to the user.
Let’s Explore Top Decentralized Bridges
Blockchain bridges have taken the world by storm; they provide the much-needed liquidity and interoperability in DeFi space. Let’s explore Best Decentralized Bridges:
Polygon Bridge
It is a decentralized, non-custodial bridge that allows users to transfer assets between the Ethereum and Polygon blockchains. It is built on the Ethereum blockchain and uses the Polygon PoS chain to facilitate cross-chain transfers.
Polygon Bridge went live in March 2021 and has since processed over $10 billion in cross-chain transfers. It is one of the most popular DeFi bridges and is used by a number of DeFi applications on both the Ethereum and Polygon ecosystems.
Here are some of the benefits of using Polygon Bridge:
- Low fees: Polygon Bridge offers low fees for cross-chain transfers.
- Fast transactions: Polygon Bridge transactions are processed quickly.
- Security: Polygon Bridge is a secure way to transfer assets between blockchains.
- Interoperability: Polygon Bridge can be used to connect to other blockchains.
Gravity Bridge
It is a decentralized, trustless bridge between the Ethereum and Cosmos ecosystems. It allows users to transfer assets between these two blockchains without the need for a centralized intermediary.
Gravity Bridge is built on the Cosmos SDK and uses the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol to facilitate cross-chain transfers. It is a non-custodial bridge, which means that users retain control of their assets at all times.
Gravity Bridge went live in March 2022 and has since processed over $10 billion in cross-chain transfers. It is one of the most popular DeFi bridges and is used by a number of DeFi applications on both the Ethereum and Cosmos ecosystems.
Here are some of the key features of Gravity Bridge:
- Non-custodial: Users retain control of their assets at all times.
- Secure: Gravity Bridge is built on the Cosmos SDK and uses the IBC protocol, which are both considered to be secure protocols.
- Scalable: Gravity Bridge is designed to be scalable, so it can handle a large volume of transactions.
- Interoperable: Gravity Bridge can be used to connect to other blockchains, such as Binance Smart Chain and Polygon.
hBTC
hBTC is a cross-chain bridge that allows users to transfer Bitcoin (BTC) between the Bitcoin and Huobi Eco Chain (HECO) blockchains. It is a semi-custodial bridge, which means that users do not need to trust the hBTC team with their assets, but they do need to create an account on the hBTC platform.
hBTC works by using a two-way peg mechanism, which means that there is a one-to-one relationship between the BTC on the Bitcoin blockchain and the hBTC on the HECO blockchain. When a user wants to transfer BTC from Bitcoin to HECO, they deposit the BTC on the Bitcoin blockchain and mint hBTC on the HECO blockchain. When a user wants to transfer hBTC from HECO to Bitcoin, they burn the hBTC on the HECO blockchain and redeem BTC on the Bitcoin blockchain.
hBTC is secured by a network of validators who stake their hBTC to secure the network. The validators are responsible for verifying transactions and ensuring that the bridge is secure.
tBTC
tBTC bridge is a cross-chain bridge that allows users to transfer Bitcoin (BTC) between the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains. It is a non-custodial bridge and uses a two-way peg mechanism. tBTC BRIDGE is a secure and reliable way to transfer Bitcoin between the Bitcoin and Ethereum blockchains. It is a newer bridge than the JustCrypto Bridge, but it has been well-received by the community and has a growing user base.
Features of tBTC
- Collateralization: tBTC is collateralized by Bitcoin, which means that there is always enough Bitcoin backing the tBTC in circulation.
- Liquidity: tBTC is liquid, which means that it can be easily bought and sold on exchanges.
- Governance: tBTC is governed by a community of stakeholders, which means that users have a say in how the protocol is developed.
Get Obligation Free Quote
[widget id=”custom_html-3″]
Nerve Bridge
Nerve Bridge is a cross-chain bridge that allows users to transfer assets between multiple blockchains, including Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, Polygon, and Nerve Network. It is a non-custodial bridge and uses a two-way peg mechanism.
Benefits of Nerve Bridge:
- Faster transactions: Nerve Bridge uses a Layer-2 solution called Nerve DEX to make transactions faster and cheaper.
- Efficient gas fees: Nerve Bridge uses a gas optimization mechanism to reduce gas fees.
- Cross-chain liquidity: Nerve Bridge provides cross-chain liquidity, which means that users can easily swap assets between different blockchains.
- Governance: Nerve Bridge is governed by a community of stakeholders, which means that users have a say in how the protocol is developed.
Final Words
In conclusion, the best cross chain bridges stand at the forefront of innovation in the ever-evolving landscape of decentralized finance. Through this comprehensive guide, we have explored how DeFi bridges enable the seamless movement of assets and data between disparate blockchain networks. They have unlocked new realms of opportunity by fostering interoperability, increasing liquidity, and expanding the accessibility of decentralized financial services.
As blockchain technology continues to mature, DeFi bridges will play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of finance. Their ability to bridge the gap between different blockchains, enhance cross-chain asset transfers, and optimize yield farming strategies holds immense promise for DeFi enthusiasts and the broader financial industry. By choosing the right bridge and doing your research, you can ensure that your funds are safe and that you are able to use the bridge to its full potential.
Choose the best DeFi development company to kickstart your innovative DeFi project.





