
Why Retailers like Lidl are Betting Big on Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
March 26, 2025
How Ripple’s Regulatory Win Accelerates Blockchain Solutions in Dubai
March 26, 2025Today, businesses across various industry verticals strive to reduce their carbon footprint and align with global climate goals. As a result, they experiment with new technologies and concepts that can help them achieve net-zero emission goals. For decades, the existing centralized carbon offset systems have served as the primary method for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, the limitations of these systems have become increasingly apparent, paving the way for advanced approaches like blockchain-based carbon credits.
Blockchain provides a competitive edge to industries worldwide through its decentralized and immutable attributes. With blockchain, businesses gain access to a modern solution that fuels operational efficiency while ensuring environmental sustainability. In this blog, we delve into the details of both traditional carbon offsetting and blockchain-based carbon credit systems. We’ll compare their mechanisms, outline their unique advantages, and decide which aligns best with your business’s sustainability strategy.
Understanding the Carbon Offset System
Carbon offset systems have long been the go-to solution for companies looking to compensate for their emissions. These systems operate by funding projects that reduce or avoid carbon dioxide, such as reforestation, renewable energy installations, or methane capture initiatives. In return, companies receive carbon credits, each representing one metric ton of CO2 equivalent (tCO2e) mitigated.
Existing carbon offset systems rely heavily on centralized entities like project developers, verifiers, registries, and brokers, which creates a multi-layered ecosystem that businesses need to navigate to offset their emissions.
How Does Existing Carbon Offsetting Work?
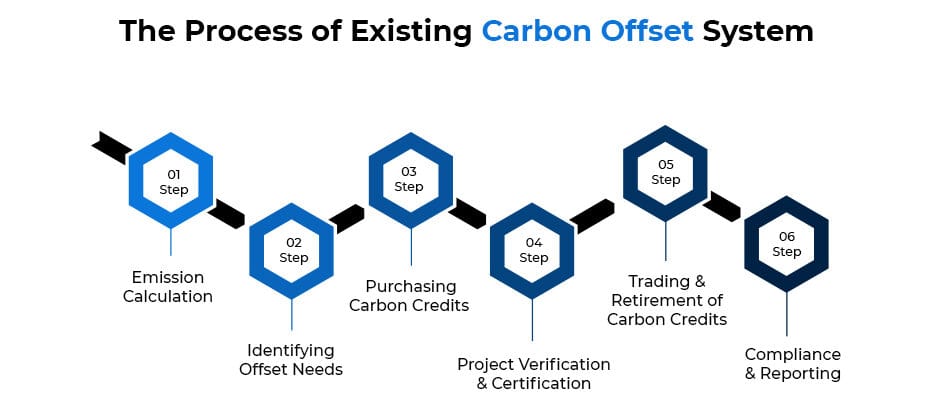
Step 1: Emission Calculation
The process begins by calculating a company’s or individual’s total carbon emissions from activities, such as manufacturing, transportation, or energy consumption. This calculation is conducted using carbon footprint calculators, analyzing energy usage data, or reports from environmental agencies. The total emissions are measured in metric tons of CO₂ equivalent (tCO₂e).
Step 2: Identifying Offset Needs
Once the carbon emission calculation is done, the next step is determining how many carbon credits are required to offset the emissions. Each credit represents one metric ton of CO2 reduced or removed (or one carbon credit = One ton of CO₂ removed or avoided). The company decides how much of its emissions to offset (full or partial).
Step 3: Purchasing Carbon Credits
The company purchases carbon credits from certified offset projects that reduce or remove CO₂. These projects include reforestation, renewable energy (wind, solar), carbon capture, and methane reduction initiatives. Transactions typically occur through brokers, registries, or carbon exchanges like Verra (VCS), Gold Standard, or CDM (Clean Development Mechanism).
Step 4: Project Verification & Certification
Offset projects undergo third-party verification by organizations like Verra, Gold Standard, or UNFCCC. These organizations assess whether the project:
- Actually reduces CO₂ emissions
- Follows international carbon offset standards
- Is not double-counted or fraudulent
If approved, the project is certified, and carbon credits are issued.
Step 5: Trading & Retirement of Carbon Credits
Carbon credits are traded in regulated or voluntary carbon markets. Companies can buy and sell credits through government-regulated programs (e.g., EU Emissions Trading System) and voluntary carbon markets (e.g., Climate Action Reserve). Once a company uses a credit to offset emissions, it is retired and cannot be resold. Retiring means these credits cannot be resold or reused. This practice ensures that the offset is legitimate and accounted for.
Step 6: Compliance & Reporting
This step involves companies reporting their carbon offset activities in sustainability reports for regulatory compliance. Some companies voluntarily offset their emissions to achieve carbon neutrality, while others do it to comply with government policies. Reports are further audited by regulators, investors, or stakeholders.
Loopholes in the Existing Carbon Offset System
1. Lack of Transparency and Traceability
The carbon offset process involves multiple intermediaries, such as brokers, certification bodies, and regulatory agencies. Hence, tracking the actual impact of an offset project is challenging. Since most transactions happen in centralized registries, it is difficult to verify whether a carbon credit has been properly issued or retired. This centralization makes it vulnerable to fraud, where companies might claim carbon reductions that do not exist.
2. Risk of Double Counting
Double counting occurs when the same carbon credit is sold multiple times or claimed by multiple entities. For instance, a government agency might include the emission reductions from a renewable energy project in its national reporting, while the same credits are sold to a company for offsetting its emissions. This undermines the credibility of the system, as the same emission reduction is being used twice.
3. High Costs Due to Intermediaries
The carbon offset programs involve numerous intermediaries, including third-party verifiers, brokers, and certification agencies. Each of these entities charges fees for its services, which makes the overall process expensive. These additional expenses restrict small businesses from participating in offset programs.
4. Delayed Verification and Issuance
The verification process for traditional carbon credits can take months or even years due to the bureaucratic nature of certifying emissions reductions. Projects must undergo rigorous documentation, auditing, and third-party verification before credits are issued. This slow process discourages companies from participating and delays the funding needed for climate action projects.
5. Difficulty in Measuring Actual Impact
Many carbon offset projects, such as reforestation and renewable energy, are designed to reduce future emissions rather than offset current emissions. However, the actual impact of these projects is difficult to measure accurately. For example, a reforestation project may plant trees, but those trees take years to absorb CO₂, and factors like wildfires or illegal logging can reduce their effectiveness. This uncertainty makes it hard to quantify the true impact of carbon offset initiatives.
6. Greenwashing and Misuse of Credits
Many corporations use carbon credits as a tool for greenwashing (claiming to be sustainable without making real efforts to reduce emissions.) Instead of genuinely cutting down their carbon footprint, some companies purchase cheap or low-quality offsets to maintain their business-as-usual operations. This diminishes the purpose of carbon offsetting, as it allows companies to continue polluting while appearing environmentally responsible.
7. Fraud and Corruption Risks
Since the traditional system operates with centralized authorities and private registries, there is potential for corruption and fraudulent activities. Some organizations have been caught selling fake carbon credits or exaggerating the emission reductions of their projects. There is an urgent need for an immutable, tamper-proof system that can prevent fraud.

Blockchain-Based Carbon Credit- Decentralizing Carbon Offsetting
Blockchain-based carbon credit systems operate through a decentralized and transparent process that enables efficient tracking, validation, and trading of carbon credits. Blockchain technology is making waves in the sustainability sector due to its advanced features. Leveraging blockchain for carbon credits is a wise approach to address the shortcomings of traditional systems.
Companies like IBM, Microsoft, and startups such as Veridium and ClimateTrade are already making buzz by offering platforms that tokenize carbon credits for seamless trading. For businesses, this blockchain-based carbon credit trend signals a shift toward more accountable and cost-effective carbon management.
How Does a Blockchain-Based Carbon Credit System Work?
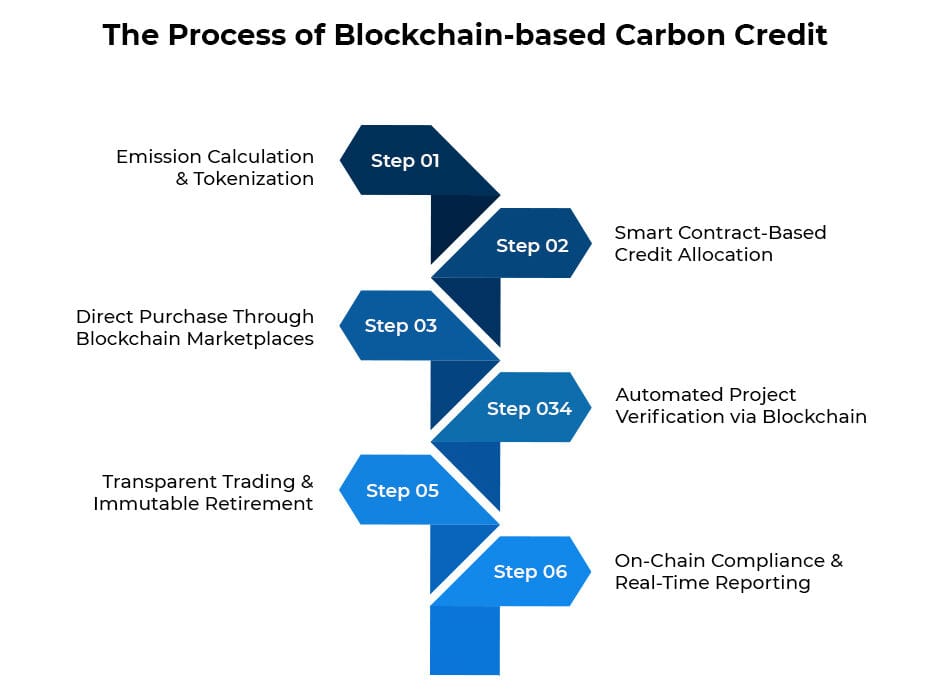
Step 1: Emission Calculation & Tokenization
Similar to traditional systems, companies calculate their carbon emissions using energy data and carbon footprint calculators. However, in blockchain-based carbon credit systems, emissions data is recorded on a decentralized ledger for transparency. Each verified metric ton of CO₂ is tokenized into a digital carbon credit.
Step 2: Smart Contract-Based Credit Allocation
Instead of manually determining offset needs, blockchain uses smart contracts to automate credit allocation. Companies specify their offset goals and smart contracts execute transactions for accurate, real-time tracking of carbon credits without intermediaries.
Step 3: Direct Purchase Through Blockchain Marketplaces
Companies purchase tokenized carbon credits directly from decentralized carbon credit platforms like Toucan, KlimaDAO, or Moss. These platforms eliminate the need for brokers, reduce costs, and improve accessibility. Transactions are recorded on-chain and enhance traceability.
Step 4: Automated Project Verification via Blockchain
Traditional verification relies on third-party audits, but blockchain-based carbon offset enhances this with real-time tracking and automated validation. IoT devices, satellites, or AI-powered verification systems feed live project data onto the blockchain to increase accuracy and prevent fraud. Smart contracts validate compliance with carbon offset standards.
Step 5: Transparent Trading & Immutable Retirement
Carbon credits can be traded on decentralized exchanges without intermediaries. Every transaction is recorded on an immutable blockchain ledger that prevents double-counting or fraud. When a credit is used, it is permanently burned (removed from circulation) through smart contracts. Hence, one can experience a transparent and auditable offset process.
Step 6: On-Chain Compliance & Real-Time Reporting
Instead of manually submitting sustainability reports, blockchain automates compliance through real-time, publicly accessible records. Companies and regulators can instantly verify emissions reductions via blockchain explorers, which improves accountability and eliminates the risk of data manipulation.
Prominent Advantages of Blockchain-based Carbon Credit System
1. Enhanced Transparency and Traceability
Every carbon credit transaction recorded on an immutable and decentralized ledger is time-stamped, and publicly accessible. Unlike traditional systems where credits are stored in private registries, blockchain-based carbon credit allows anyone to track the lifecycle of a carbon credit and experience complete transparency. This eliminates the risk of manipulation, fraud, or hidden transactions.
2. Elimination of Double Counting
Blockchain-based carbon credit systems also prevent one of the biggest issues in traditional carbon markets, i.e., double counting. It assigns each credit a unique digital identity (tokenized carbon credits), which ensures that once a credit is used (retired), it cannot be resold or claimed again.
3. Reduced Costs and Faster Transactions
Traditional carbon offset systems involve brokers, verifiers, and multiple intermediaries, which increase administrative costs and slow down the process. Blockchain-based carbon credit system automates transactions using smart contracts and enables direct peer-to-peer trading of carbon credits. It removes middlemen, reduces costs, and speeds up verification and issuance of carbon credits.
4. Real-Time Verification and Auditing
With traditional carbon credits, verification can take months or years, delaying funds for climate projects. Blockchain-based carbon credit encourages real-time verification of carbon offset activities through IoT sensors, satellite data, and AI-powered analysis, which automatically update records on the blockchain. This ensures that companies get instant proof of emission reductions without delays.
5. Greater Accessibility and Inclusivity
Blockchain removes barriers to entry, allowing small businesses, individuals, and community-led projects to participate in carbon markets without needing expensive certifications. With tokenized carbon credits, even a small-scale project can issue verified credits and sell them globally, promoting fair participation.
6. Fraud Prevention and Data Security
Since blockchain records cannot be altered or deleted, it prevents fraud and false claims in carbon offset programs. Additionally, all transactions are verified through consensus mechanisms before being added to the ledger, while only legitimate credits are issued.
7. Interoperability with Global Carbon Markets
Traditional carbon offset systems vary by region and regulatory body which makes it difficult to trade across borders. Blockchain’s decentralized nature allows for seamless integration between different carbon markets that improves liquidity and cross-border trading of credits.
Conclusion
Choosing between traditional carbon offset systems and blockchain-based carbon credits becomes pivotal when it comes to achieving a net-zero emission target. However, current carbon offsetting systems face significant challenges that can hinder B2B sustainability efforts. Blockchain-based carbon credits, on the other hand, offer a forward-thinking solution that combines transparency, cost-effectiveness, and technological innovation to meet the demands of a digital-first world. For business decision-makers, the shift to blockchain means future-proofing carbon management strategies. If you’re planning to invest in a blockchain-based carbon credit system, reach out to Antier today!
Antier is a leading blockchain carbon credit development company, specializing in building secure and transparent carbon credit solutions for businesses seeking a way to achieve a sustainable future. Whether you need a custom carbon marketplace, automated smart contract workflows, or a full-fledged carbon tracking platform, Antier provides end-to-end blockchain solutions that empower businesses to build trust, transparency, and efficiency in their carbon offset initiatives.
Contact our team today for blockchain carbon credit platform development support!



