The vital element missing in the intricate web of the global supply chain is trust. As a consumer, it is nearly impossible to determine the quality of the product available in the market. This uncertainty fuels concerns not only related to food safety and authenticity but also to the integrity of the food supply chain.
The complex food supply chain management can adversely affect public health. From food contamination to food-borne illness, and inadequate quality control to counterfeit products, several key issues are the outcome of an inefficient food supply chain.
However, Blockchain development for food supply chain has emerged as a digital revolution that promises to restore trust and transparency in the processes. The technology enables consumers and stakeholders to track and trace the food journey from the farm to the market. Such unprecedented transparency, accountability, and security help businesses build a more efficient food network and eliminate bottlenecks in the supply chain. Companies like Nestle, Walmart, Golden State Foods, and more are experimenting with the food supply chain Blockchain solutions.
In this blog, we will cover in-depth the problems in the existing food supply chain and how Blockchain development for supply chain is a strategic move.
How Traditional Food Supply Chain Model Works
Challenges in the Traditional Food Supply Chain
The traditional food supply model faces several key issues, such as
- Lack of Transparency: The consumer is unaware of where their food comes from, how it was produced, and whether it meets the quality standards or not.
- Complex Distribution Network: The traditional supply chain involves multiple intermediaries between the producer and the consumer, which makes the process complex. This complexity leads to delays and inefficiencies.
- Inadequate Traceability: Tracing the origin of a food product in a traditional supply chain is challenging in the event of food recalls or quality issues that put consumers at risk.
- Quality and Nutritional Loss: Product in the traditional supply chain model goes through a long process to reach the end consumer which reduces the product quality and nutritional value.
- Delays and Increased Costs: The traditional food supply chain model involves cumbersome paperwork, manual record-keeping, and a lot of intermediaries that result in delays and further increase operational costs.
- Lack of Trust: The conventional food supply chain often lacks trust as it involves various parties and increases the risk of counterfeiting or fraudulent products entering the system.
Major Food Safety Concerns in Traditional Food Supply Chain System
- Food Fraud
The complicated food supply chain network increases the risk of food fraud that affects public health. A major food safety incident in China was highlighted in 2008, when 300,000 Chinese infants and young children were affected with kidney and urinary tract, including kidney stones. Melamine was used in diluted raw milk at milk-collecting stations to boost its protein content. This incident illustrated the complexity of the trade of food products.
- Foodborne Illness
According to a WHO report, out of 600 million people in the world, 1 in 10 people fall ill after consuming contaminated food. Such food contains harmful bacteria, parasites, viruses, or chemical substances that can cause more than 200 diseases. A strong supply chain system can help ensure food safety.
- Food recalls
The inefficient supply chain also leads to food recalls. The term food recalls refers to the removal of foods from the market that violate FDA (Food and Drug Administration) regulations. A survey conducted in 2010 shows that the coverage cost of the food recall is $10 million. Big brands such as Pepsi, Coca-Cola, Nestle, Cadbury, etc., have suffered losses due to the food recalls.
So, how can these problems be resolved? The answer is Blockchain.

Blockchain-based Food Supply Chain: An Introduction
A Blockchain is a distributed ledger in which transactions are recorded in blocks, and each block is identified with a cryptographic hash of data. Hence, it is nearly impossible to change the data from this hash. Any change in the transaction data will create a different hash with each block hash that is included as a data point in the next block. Blockchain provides a secure ecosystem where data tampering is difficult.
Blockchain enables users to create and share a ledger of transactions with all participants in the value chain. It creates a single source of truth of information and provides a real-time unified view of the whole supply chain. Blockchain development for food supply chain is a strategic approach as it helps resolve several food ecosystem issues, including uncertainty regarding the origin of products, tracking of ingredients, and enhancing sustainability. Blockchain has the potential to resolve all these problems bringing maximum level of transparency and traceability into the entire supply chain.
Global Market Forecasts of Blockchain Development for Food Supply Chain
According to the Global News Wire, the global Blockchain in agriculture and food supply chain market size is estimated to be USD 133 million in 2020 and is expected to reach USD 948 million by 2025 at a CAGR of 48.1 percent during the forecast period.
This report shows that the use of food supply chain Blockchain solutions will grow in the coming years and revolutionize the industry’s supply chain management to a great extent with its quality traits. Today, businesses in the food industry strive to achieve maximum supply chain efficiency, and Blockchain development for food supply chain has emerged as a vital tool to achieve their goals.
How Blockchain-based Food Supply Chain Works
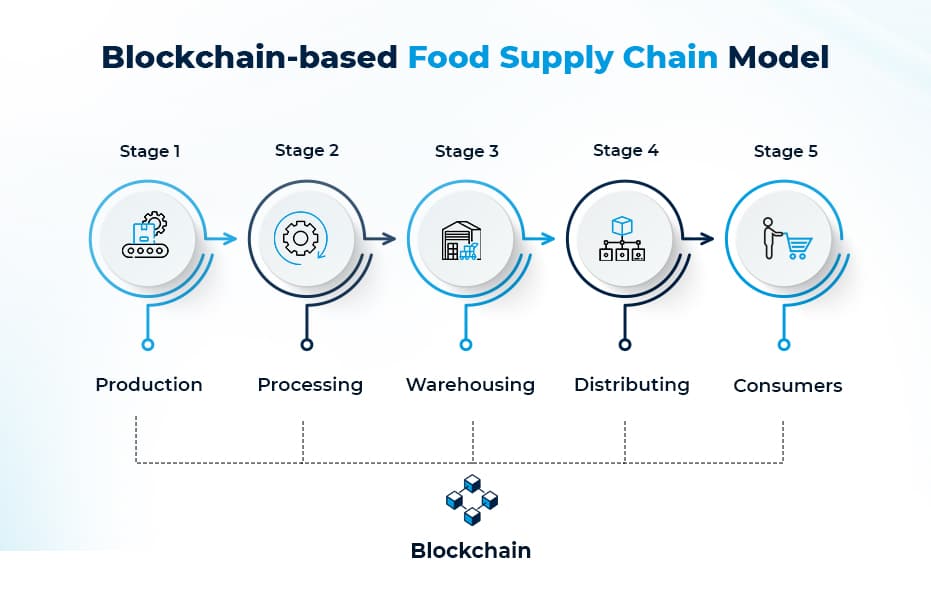
Stage 1: Farmers store information on the Blockchain
The food supply chain Blockchain solutions enable farmers to store the grown-up crop information, such as origin and type of crop, harvest data, the process followed for sowing, storage and handling data, and more, on Blockchain through their mobile application or center location on the Blockchain. This information can easily be fetched by all parties involved within the network.
Farmers can also upload images of the crop to help factories or production companies make informed decisions about the quality of the crop. The smart contracts include the regulations that help ensure whether compliance is met while feeding the data on Blockchain or not.
Stage 2: Food processing companies record the processing details on the Blockchain
Once the crops are grown, they are sent for the next stage, i.e., processing to factories or food processing companies. These companies bid for the crops through smart contracts. Once the bid is done, they begin the food processing and store the related information on the public Blockchain. This information helps retailers and consumers determine if the food has been appropriately processed or not. As the regulations are added to smart contracts, food compliance will be followed at every step of food processing.
Stage 3: Wholesalers bid for the processed products using smart contracts
Once the food item is fully processed by companies, they are put out for bidding. Wholesalers bid through smart contracts. After the company accepts the bid, food processing companies ship the processed food items to the wholesaler. Parties involved within the food supply chain Blockchain system can track the product journey at each stage without worrying about security.
Stage 4: Finished products are shipped through IoT-enabled vehicles to retailers
When the wholesaler receives the food items, they hire a logistic service provider to distribute the products to retailers. The food products are further transported through IoT-enabled vehicles that keep these items safe under a controlled temperature, reduce the risk of food spoilage, and maintain the quality of the product. The sensors in the IoT vehicles send real-time information of the temperature of food items as well as their location to the Blockchain. This information recorded on food supply chain Blockchain solutions helps retailers to keep track of the food items they are going to receive.
Stage 5: Consumers receive the final product
Blockchain development for food supply chain is a game-changer as it brings transparency from source to destination. The information of food products processed within the Blockchain-based supply chain system, such as transportation details, batch numbers, factory and processing data, farm origination details, storage temperature, expiration details, etc., are recorded on Blockchain at every stage. All transactions are also validated by stakeholders involved in the network to form a consensus. As the end consumers can access the product information and trace its journey, they can quickly decide if they should buy a specific food item or not.
Benefits of Blockchain Development for Food Supply Chain
The following points show the benefits of Blockchain development for food supply chain.
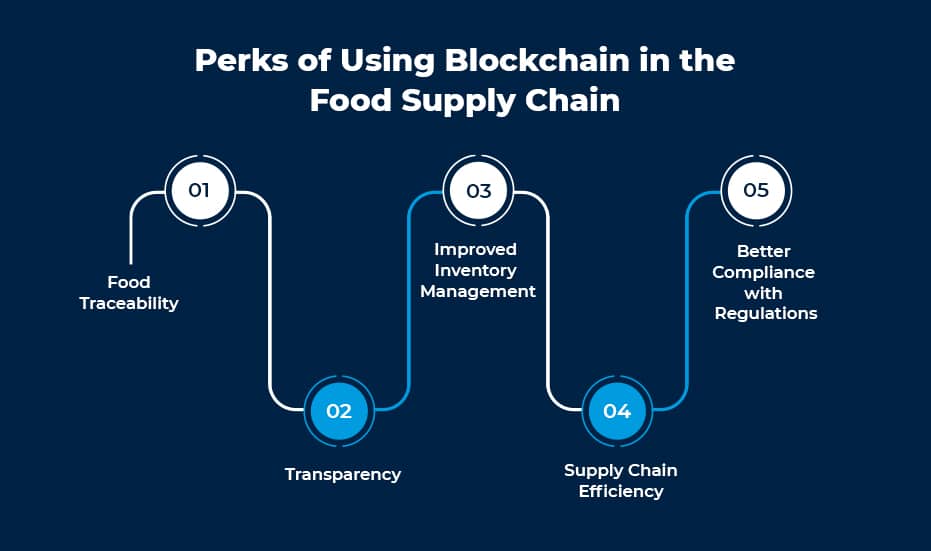
- Food Traceability
Blockchain development for food supply chain is an innovative approach for achieving end-to-end traceability into the system. This distributed ledger technology allows users to track the journey of food items from farm to fork and gain access to information, such as the product origin, production methods, transport and storage conditions, and more. This traceability reduces the risk of food fraud and recalls, and improves food safety and quality.
- Transparency
Food supply chain Blockchain solutions provide a shared record of all transactions. Hence, it increases transparency in the supply chain and bolsters trust among different parties, such as farmers, processors, wholesalers, retailers, and consumers. Anyone with permission can verify the information about a product on this shared ledger. The transparency in the food supply chain also helps identify and address the issues related to food quality, safety, and sustainability.
- Improved Inventory Management
The role of food supply chain Blockchain solutions can also be observed in improving inventory management. It enables real-time tracking of food products throughout the supply chain and allows stakeholders to easily predict demand and reduce waste. It also helps reduce several common issues, such as double-counting or underestimating inventory levels.
- Supply Chain Efficiency
Blockchain development for food supply chain helps streamline various processes. It reduces the time required for manual record-keeping and data sharing. Additionally, it eliminates the need for brokers, distributors, or other intermediaries in the food supply chain, reducing the cost, and bringing maximum efficiency as transactions can be done in a faster and secure manner.
- Better Compliance with Regulations
The immutable records and data are readily available for audits and inspections with Blockchain which further helps in complying with several regulatory requirements. Additionally, the technology also ensures that sensitive data, such as compliance and quality reports are stored securely and easily accessible to authorized parties.

Top Companies Utilizing Food Supply Chain Blockchain Solutions
The following are some big brands that have already empowered their food supply chain with Blockchain integration.
- Bumble Bee Foods
Bumble Bee Foods is one of the largest seafood companies in North America that incorporated SAP Blockchain technology to enhance the traceability of its production. This innovative step by the company allows consumers to trace the journey of yellowfin tuna from the Indonesian ocean to the customer’s dinner table through smartphones and QR codes on product packaging.
- Nestlé
The food giant, Nestle is among the early adopters of Blockchain that partnered with the IBM Food Trust to improve the traceability of Rainforest Alliance-certified coffee brand, Zoégas. The company is also using the OpenSC platform in order to track the supply of New Zealand milk to Nestle factories in the Middle East.
- Tyson Foods
Tyson Foods is a leading protein-focused food company that is utilizing Blockchain technology, partnering with FoodLogicQ. They are able to track and report on quality issues across their supply chain and address them immediately to drive product quality. The data-driven reporting enables them to make informed decisions about food quality issues.
- Walmart
The Vice President of Food Safety once asked his team to trace a package of sliced mangoes to the source. It took 6 days, 18 hours, and 26 minutes to fetch the information from their traditional system. After partnering with IBM to create a food traceability system based on the Hyperledger Fabric, Walmart would be able to trace the mangoes stored in their US stores within 2.2 seconds- it was as easy as flipping a coin.
Conclusion
Ensuring transparency and accountability across the food supply chain has now become a necessity, especially when the food contamination cases around the world have increased. Blockchain has emerged as a ground-breaking technology that helps trace contaminated products easily and stop the spread of foodborne diseases. This distributed ledger technology allows businesses to record their transactions and even granular information about food items, which helps them make informed decisions.
Implementing food supply chain Blockchain solutions into your system will help you achieve maximum visibility throughout the process. The increased visibility will help you manage suppliers better, perform efficient quality checks, and save time and costs at several stages of the supply chain.
Antier, a leading expert in Blockchain development for food supply chain, understands the power of this distributed ledger technology and hence, builds tailored solutions that meet the client’s expectations and achieve their supply chain goals. Contact us today to learn more about our food supply chain Blockchain solutions services.







